What is a Meningioma?
A meningioma is a rare kind of brain tumour. Cancer is a condition in which cells of the body start dividing uncontrollably.

A meningioma is a rare kind of brain tumour. Cancer is a condition in which cells of the body start dividing uncontrollably.
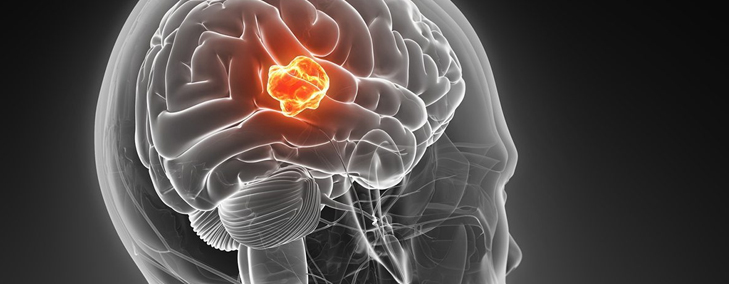
The signs and symptoms may be caused by Meningiomais due to the tumour mass pressing on surrounding structures. They include:
The following tests and procedures may be used:
The prognosis and treatment options depend on the following:
On injection into the patient, the PRRT agent targets the sits of the tumor and deposits radiation at the sites.
Some of the tests that were done to diagnose the cancer or to find out the stage of the cancer may be repeated. Some tests will be repeated in order to see how well the treatment is working. Decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop treatment may be based on the results of these tests.
Some of the tests will continue to be done from time to time after treatment has ended. The results of these tests can show if your condition has changed or if the cancer has recurred (come back). These tests are sometimes called follow-up tests or check-ups.